Optimization and establishment of the DPS-based ELISA method
Volume of plasma in DPS samples
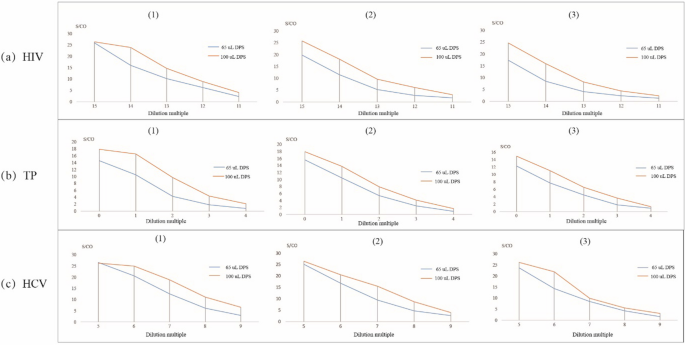
The effect of different volumes of plasma used for the DPS samples for anti-HIV, anti-TP, and anti-HCV testing is shown in Fig. 1. In all serial dilution experiments of all 3 agents, the test result curves (S/CO) using 100 µL of plasma were higher than that when 65 µL of plasma was used.
Size of DPS sample and volume of eluent
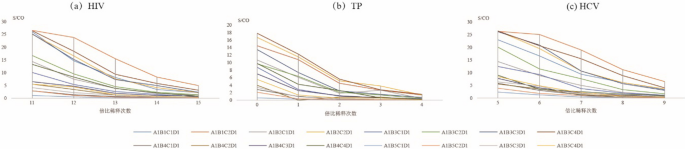
As shown in Fig. 2, for HIV and HCV the detection results (S/CO) using the combination of A1B1C2D1 were greater than those using other combinations of sample size and eluent volume (Fig. 2a, c). However, for TP, the detection results using the combination of A1B1C2D1 was lower than when the A1B3C4D1 combination was used (Fig. 2b).
Comparison of ELISA tests for detection of anti- HIV/anti-TP/anti-HCV under different combinations based on size of DPS and volume of eluent Notes: A indicates that DPS sample contained 100 µL plasma; B represents the size of DPS sample [whole spot, 1/2 DPS, 1/4 DPS, 2 discs and 1 discs (6 mm)]; C show that the volume of eluent [1 mL, 500 µL, 300 µL,200 µL]; D means the amount of sample according to test kits
Elution buffer
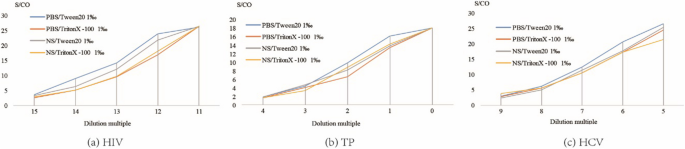
As shown in Fig. 3, the detection results for all 3 agents were the highest when PBS with 1‰ Tween20 buffer was used.
Elution time and elution temperature
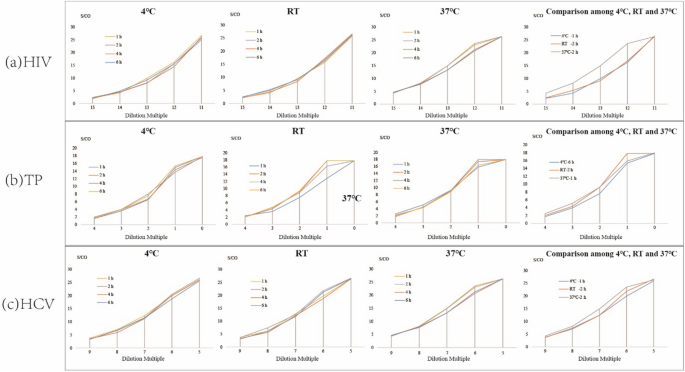
Results of the effect of different combinations of elution time and elution temperature on the performance of the DPS-based ELIA method are shown in Fig. 4. For HIV, TP, and HCV the best elution time was 2 h at RT, or 1 h at 37°C. At 4°C, the best elution times were 1, 6, and 2 h for HIV, TP and HCV, respectively. Further analysis was then performed to determine the optimized combination for the detection of all 3 agents (Fig. 4a, b, c). The results indicated that elution for 2 h at RT provided optimal detection of all 3 agents.
Optimal conditions
No statistically significant differences were observed. Based on the aforementioned experimental results, the optimal conditions for the DPS-based ELISA assay to detect all 3 agents are: plasma volume of was 100 µL, whole spot DPS size, eluent volume of the elute was 500 µL, elute of PBS with 1‰ Tween20 buffer, elution time of 2 h, and elution temperature of RT.
Evaluation of the DPS-based ELISA method to screen for HIV, TP and HCV
In order to evaluate the linear range, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and anti-jamming capacity of the DPS-based ELISA method to screen for anti-HIV, anti-TP, and anti-HCV antibodies simultaneously, laboratory panels were constructed, and the DPS-based ELISA method was tested using these panels.
Linear range
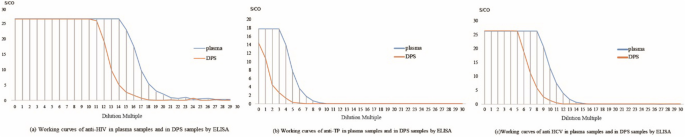
The linearity of the DPS-based ELISA method for anti-HIV, anti-TP, and anti-HCV is shown in Fig. 5. The linear range of determination for anti-HIV, anti-TP, and anti-HCV was 214 to 219 (R2 = 0.98), 23 to 27 (R2 = 0.97), and 28 to 213 (R2 = 0.98), respectively. As shown in Fig. 1, for the detection of anti-HIV, the DPS-based ELISA method was linear in the dilution range of 211 to 215, with a correlation coefficient (R2) = 0.96. For TP, the assay was linear in the dilution range of 20 to 23 (R2 = 0.96), and for anti-HCV was linear in a dilution range of 25 to 29 (R2 = 0.98). These determined linear ranges were then used for further experiments.
Sensitivity and specificity
Test results of the DPS-based ELISA method using the laboratory basic panel is shown in Table 1. Using the plasma test results as the standard, the sensitivity and specificity of the DPS-based ELISA method for anti-HIV, anti-TP, and anti-HCV were all 100%.
Analytical specificity
Results of testing the DPS-based ELISA method for the laboratory analytical specificity panel is shown in Table 2. The results showed that the method was able to identify coinfections in all of the samples tested, and that coinfections did not interfere with the ability of the method to detect other infections.
Precision evaluation
Results of the evaluation of the precision of the DPS-based ELISA assay are shown in Table 3. The inter-day, intra-assay, and inter-spot CVs for HIV were 2.10–1.53%, 0.00–3.17% and, 2.84–8.03%, respectively; for TP they were 0.20–12.31%, 0.06–7.25%, and 0.37–11.47%, respectively; for HCV they were 3.01–3.86%, 1.30–5.28%, and 4.18–12.92%, respectively. These results indicate the DPS-based ELISA method provides acceptable precision to screen for HIV, TP, and HCV.
Comparison between DPS and plasma specimens
The test result of the 619 matched plasma/DPS samples are shown in Table 4. Of the samples, 25.36% were all 3 agent negative, 17.29% were HIV mono-infected, 16.16% were TP mono-infected, 27.63% were HCV mono-infected, 4.52% were HIV/TP co-infected, 6.79% were HIV/HCV co-infected, 1.13% were HCV/TP co-infected samples, and 1.13%, HIV/HCV/TP co-infected. In the comparison of test results between plasma sample and DPS samples, only 2 pairs of DPS/plasma samples exhibited different results. The DPS-based ELISA method failed to detect 1 HCV mono-infected sample and 1 HIV/HCV/TP co-infected sample. For the HIV/HCV/TP co-infected sample, the discrepant result was for the detection of TP, and the S/CO in the plasma sample was 2.143 and in the DPS sample was 0.5. For HCV, the S/CO was 3.049 in the plasma sample and 0.878 in the DPS sample.
As shown in Table 5, the proportion of HIV-positive samples, TP-positive samples, and HCV-positive samples were 29.7% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.26–0.34), 22.9% (95% CI: 0.20–0.26), and 36.7% (95% CI: 0.33–0.41), respectively. For HIV, the DPS-based method exhibited 100% sensitivity (95% CI: 0.97–1.00) and 100.0% specificity (95% CI: 0.99–1.00). For TP, the DPS-based method had a sensitivity of 98.6% (95% CI: 0.94–1.00) and a specificity of 100% (95% CI: 0.99–1.00), and for HCV the sensitivity was 99.6% (95% CI: 0.97–1.00) and specificity was 100% (95% CI: 0.99–1.00).
Take into account the ratios of HIV-, TP-, and HCV-positive samples, the positive predictive value (PPV) of the DPS-based method was 100% for HIV/TP/HCV, and the negative predictive value (NPV) was 100% for HIV, 99.6% for TP, and 99.7% for HCV. The Kappa value between the results of plasma samples and DPS samples was 100% for HIV (p < 0.001, 95% CI: 1.00–1.00), 100% for HCV (p < 0.001, 95% CI: 0.99–1.00), and 99% for TP (p < 0.001, 95% CI: 0.98–1.00).
https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiR2h0dHBzOi8vdmlyb2xvZ3lqLmJpb21lZGNlbnRyYWwuY29tL2FydGljbGVzLzEwLjExODYvczEyOTg1LTAyMy0wMjIyNS020gEA?oc=5
2023-12-11 09:47:45Z
CBMiR2h0dHBzOi8vdmlyb2xvZ3lqLmJpb21lZGNlbnRyYWwuY29tL2FydGljbGVzLzEwLjExODYvczEyOTg1LTAyMy0wMjIyNS020gEA
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "Development and evaluation of serological screening based on one dried plasma spot for HIV, syphilis, and HCV - Virology Journal - Virology Journal"
Post a Comment